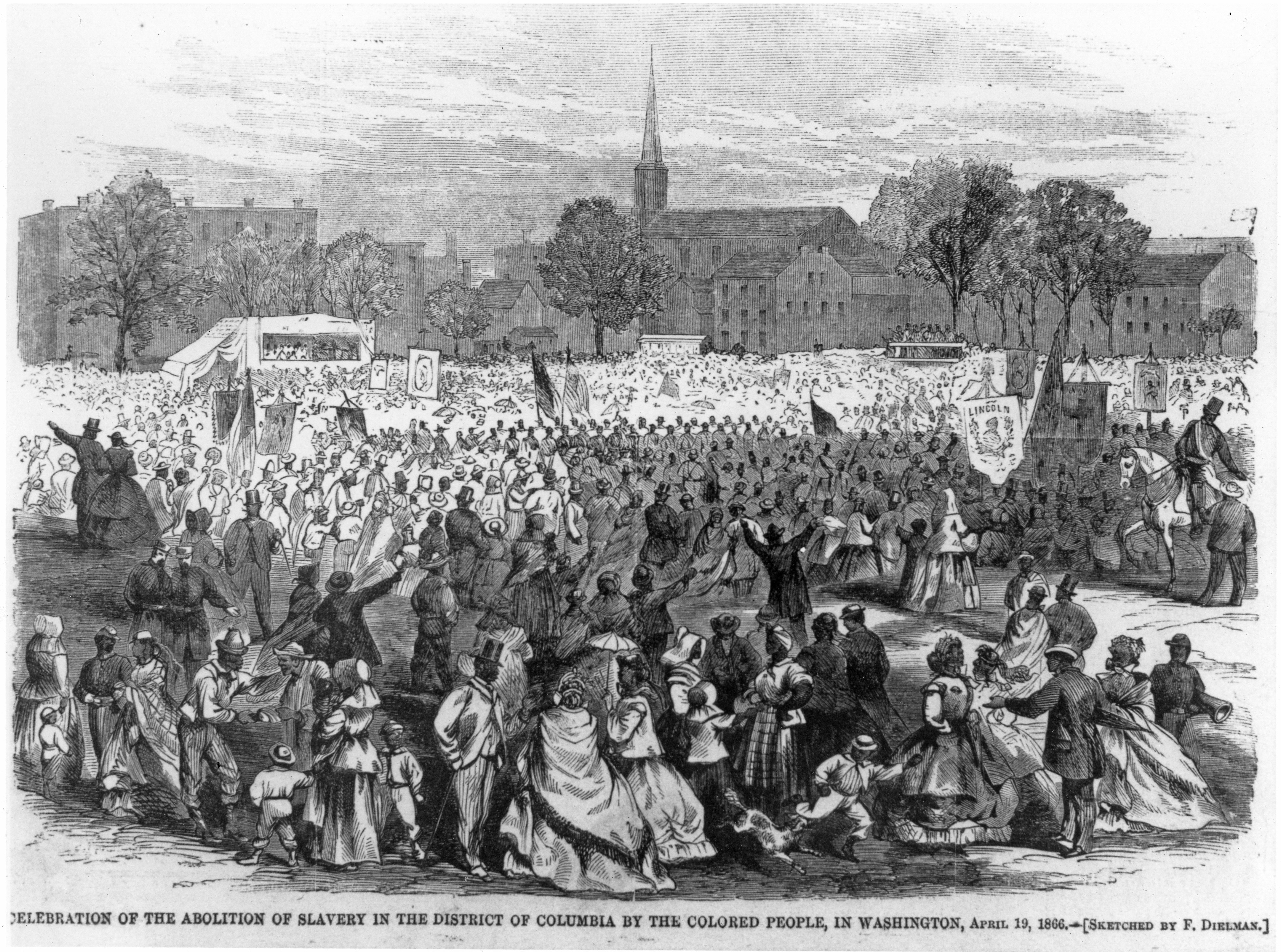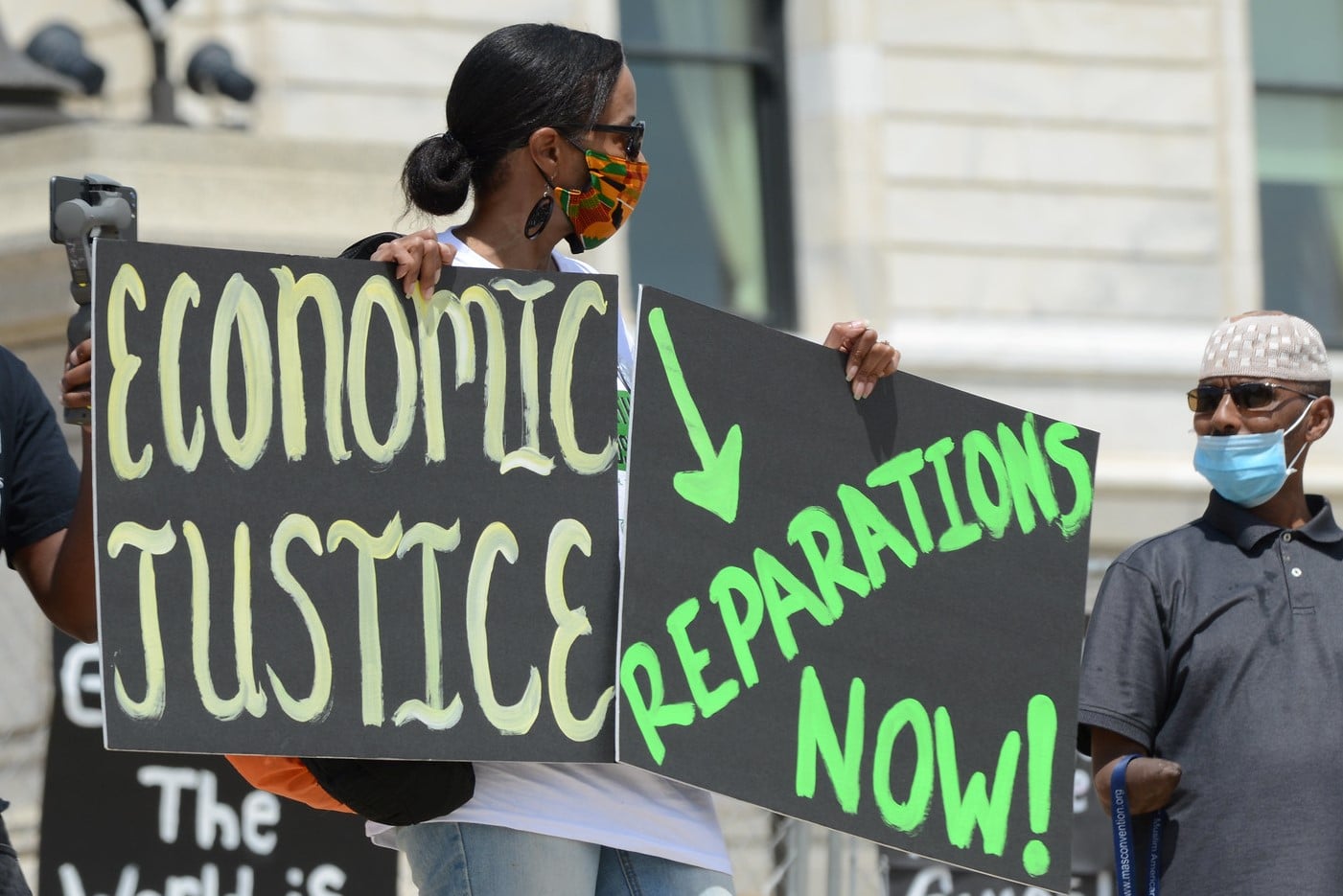The Mississippi Constitution was one of the first pieces of legislation that provided a uniform system of free public education for children regardless of race.
Continue reading
Congressman Thaddeus Stevens offered an amendment to the Freedmen's Bureau Bill to authorize the distribution of public land.
Continue reading
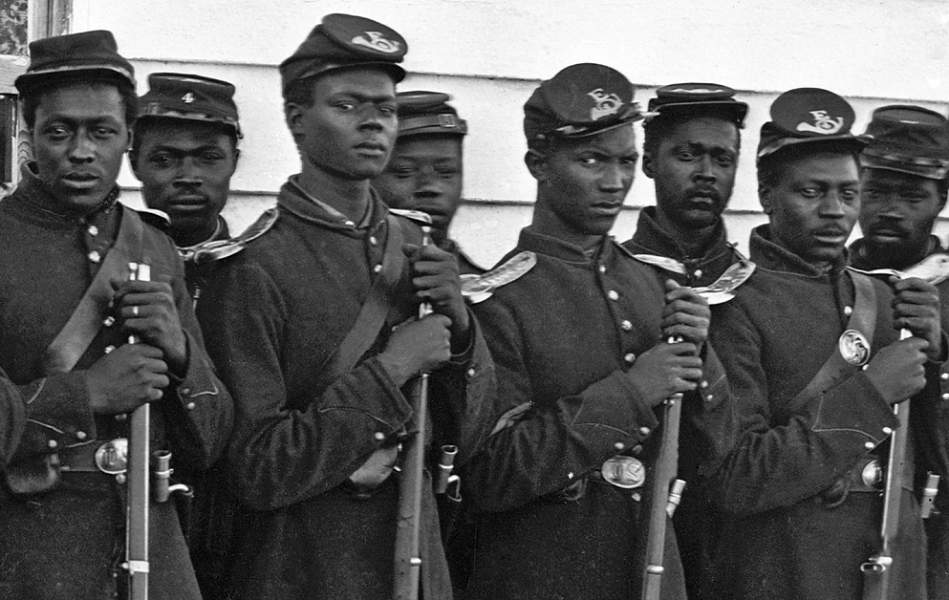
The Bureau of Refugees, Freedmen, and Abandoned Lands was established within the War Department to undertake the relief effort and social reconstruction after the Civil War.
Continue reading
The South Carolina constitutional convention met with a majority of Black delegates, adopting a constitution that provided for all people regardless of race, economic class, or gender.
Continue reading
Demands by Black ministers after the Ebenezer Creek Massacre led to the short-lived land distribution during Reconstruction known as Special Field Order No. 15.
Continue reading
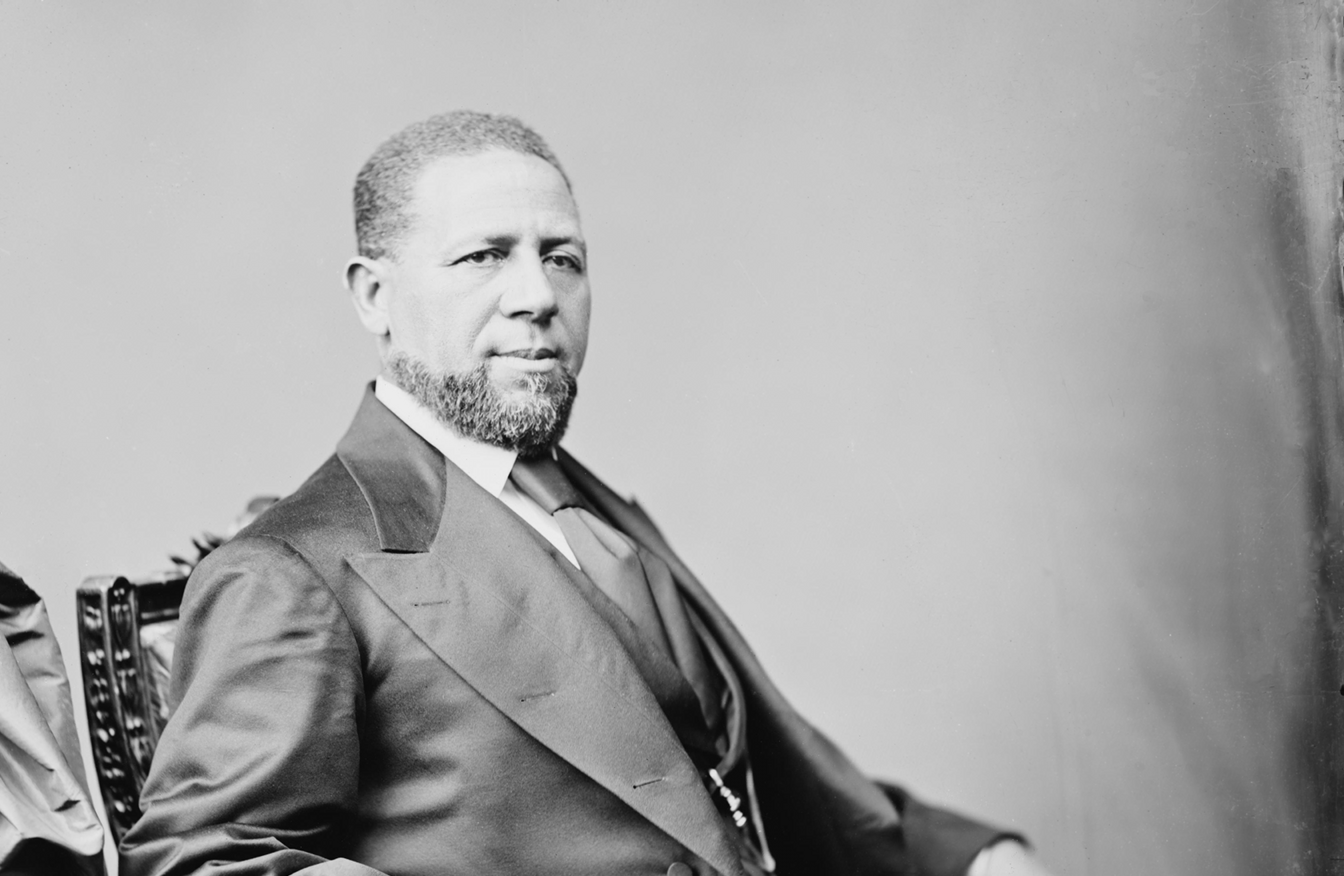
Hiram Rhodes Revels was the first African American to be elected to serve in the U.S. Senate.
Continue reading
During the Reconstruction Era, people emancipated from slavery searched for their loved ones throughout the United States and Canada. They often used "last seen" ads. This is one case of successful reunification.
Continue reading
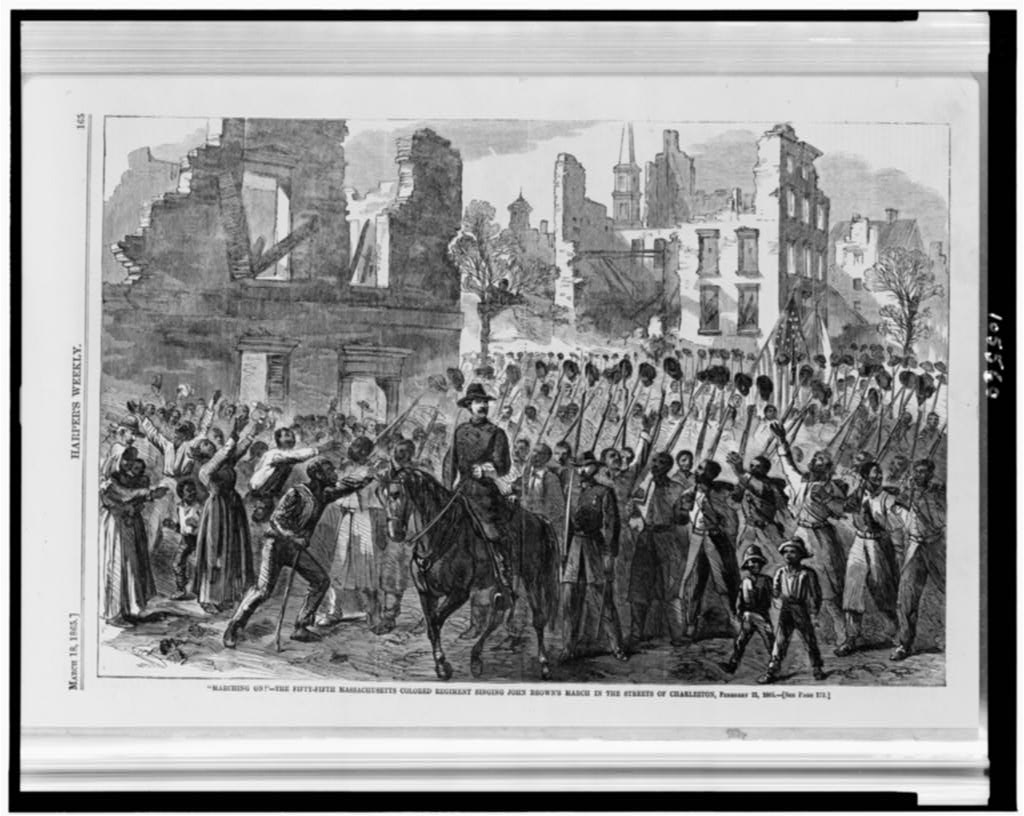
The Union Army moved into Charleston, South Carolina, the city where the Civil War had begun four years earlier.
Continue reading
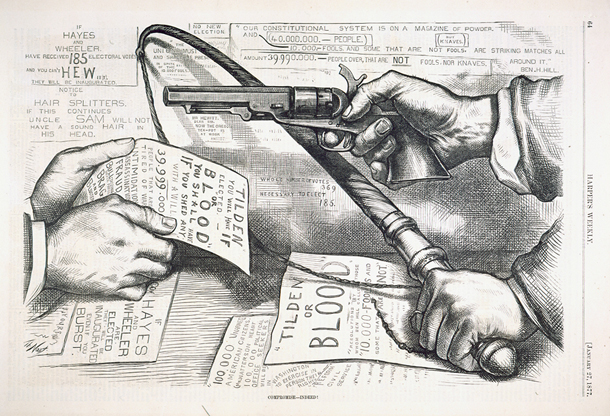
Rutherford Hayes became the 19th President of the United States with a devastating impact on Reconstruction.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Henry Louis Gates Jr. with Tonya Bolden. 2019. 240 pages.
Readers trace the rise and fall of racial equity during Reconstruction as increasingly violent white supremacy and new forms of oppression take hold at the turn of the 20th century.
Continue reading
Article. By Richard Dana.
A group of students at Kent State University-Ashtabula helped secure local recognition for Reconstruction era lawyer and writer Albion Tourgee, including a historical marker at his birthplace.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Robert B. Moore with Beryle Banfield. 1983. 40 pages.
Critique and analysis of textbook coverage of the Reconstruction era.
Continue reading
The U.S. Civil War ended when the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia surrendered to U.S. General Ulysses S. Grant at Appomattox Court House in south-central Virginia.
Continue reading
The federal government compensated the “owners” of enslaved people for their “loss of property.” The people whose labor and families were stolen for generations were not compensated nor given any assistance for the transition to freedom.
Continue reading
African Americans tested their right to vote and when denied, cast their own “freedom ballots,” on election day in Norfolk, Virginia.
Continue reading
Teaching materials and guides on the 15th Amendment's significance in 2020 — its 150th anniversary and an election year.
Continue reading
Apply for a mini-grant to teach the 15th Amendment in 2020, the 150th anniversary of the Constitutional right to vote regardless of "race, color, or previous condition of servitude."
Continue reading
Though our students' textbooks suggest otherwise, on this 150th anniversary of the 15th Amendment the struggle for ballot access is not over.
Continue reading
Teaching Activity. By Adam Sanchez. Rethinking Schools, 2020.
This multimedia, creative role play introduces students to the ways African American life changed immediately after the Civil War by focusing on the Sea Islands before and during Reconstruction.
Continue reading
Late night raid on the Charleston post office by a mob of white supremacists and the burning of abolitionist mail.
Continue reading
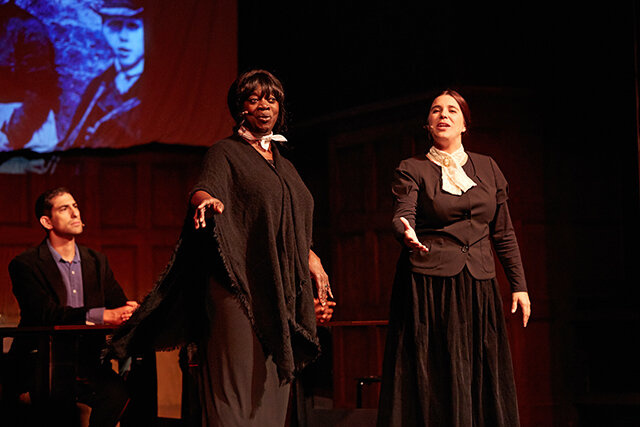
The musical "The Moment Was Now" is set in Reconstruction era Baltimore with debates about labor, women's right to vote, and the rights of African Americans.
Continue reading
Walter H. Williams was the first Black teacher appointed to a Freedmen’s Bureau School in Lafayette Parish, Louisiana during Reconstruction.
Continue reading
Teaching Activity. By Ursula Wolfe-Rocca.
In this activity, students take on the role of activist-experts to improve upon a Congressional bill for reparations for Black people. They talk back to Congress’ flimsy legislation and design a more robust alternative.
Continue reading
In a people's history online class, Professor Kidada Williams and Tiffany Mitchell Patterson discussed African American survivors of racist violence in the context of Reconstruction, drawing parallels to the contemporary moment.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Brian K. Mitchell, Barrington S. Edwards, and Nick Weldon. 2021. 256 pages.
This Reconstruction history graphic novel tells the story of Oscar James Dunn, a New Orleanian who became the first Black lieutenant governor and acting governor in the United States.
Continue reading