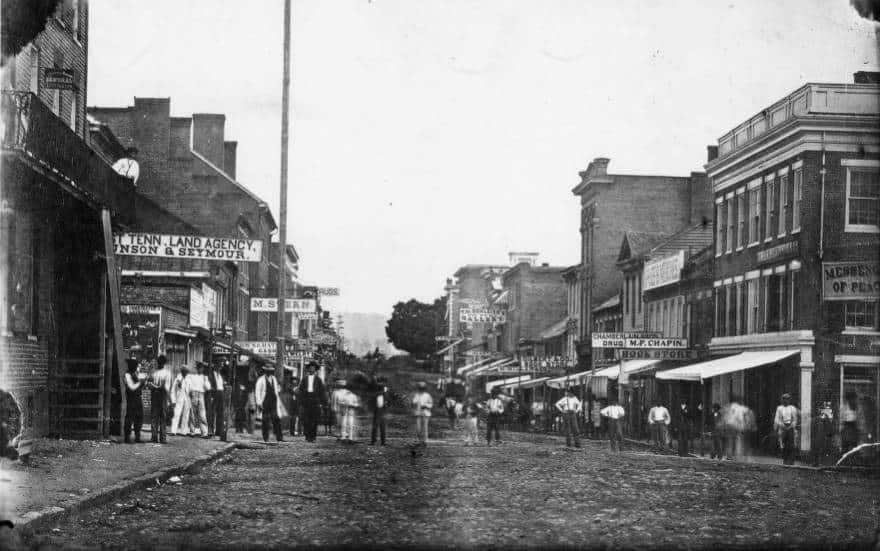
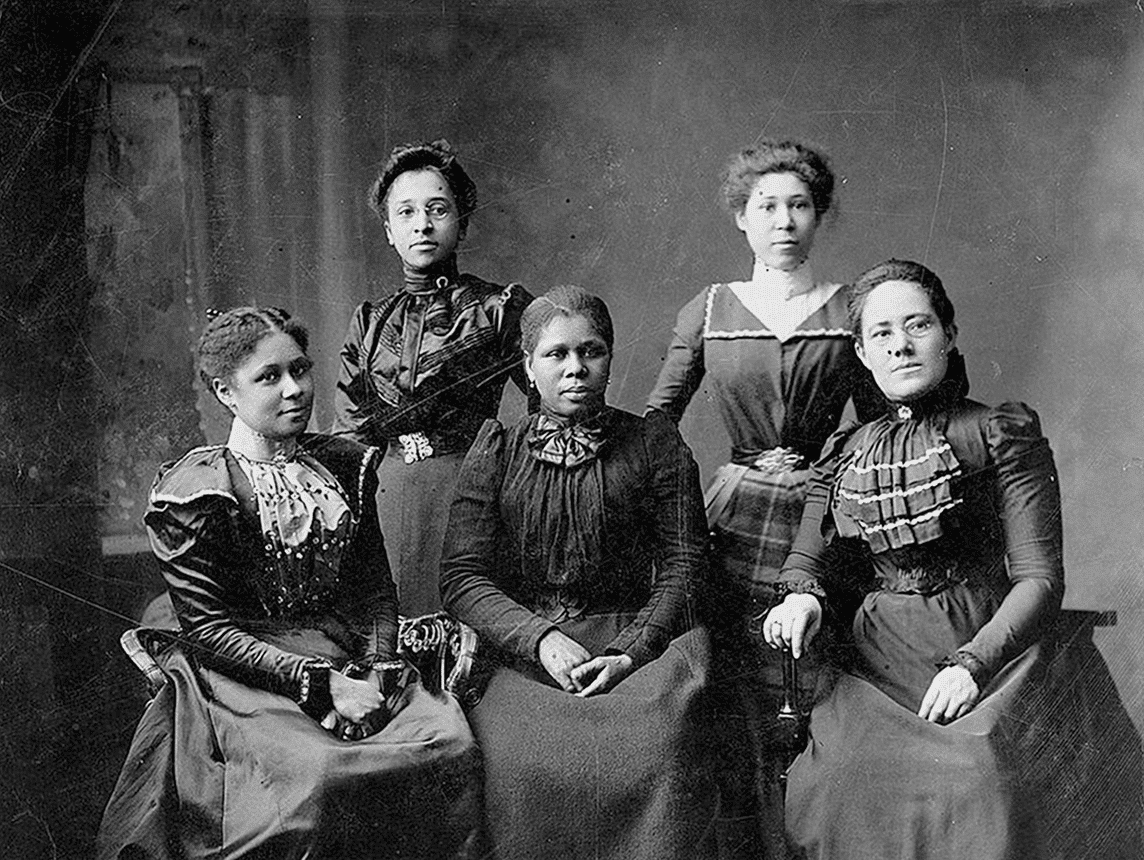
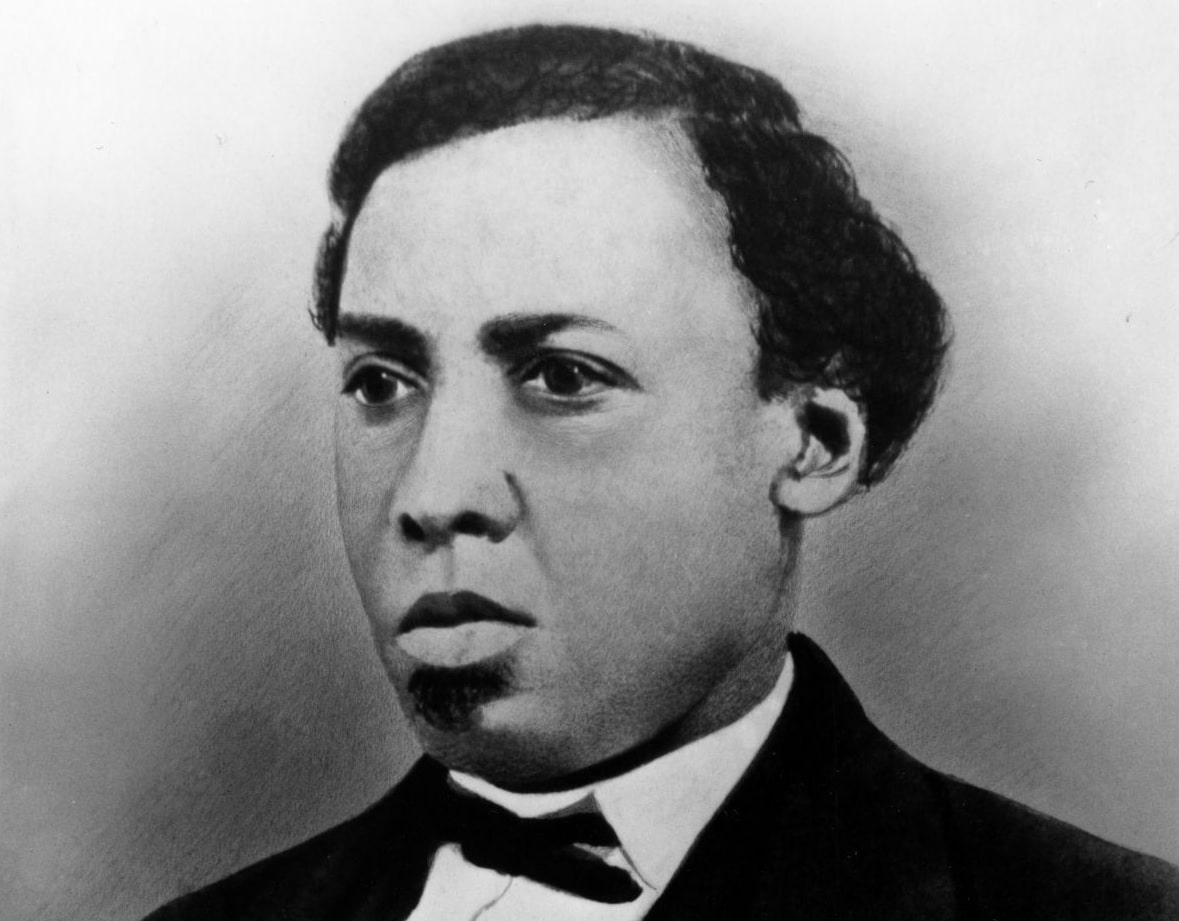
Benjamin Berry Manson and Sarah Ann Benton White, formerly enslaved in Tennessee, receive an official marriage certificate from the Freedmen’s Bureau.
Continue reading
The first “Redeemer” government is established in Tennessee after conservatives gain control of the state’s General Assembly, ushering in an era of Jim Crow segregation laws.
Continue reading
U.S. Senator Cragin spoke against delaying the expansion of suffrage. He countered the statements by white Democrats, saying the real reason they were opposed to Black suffrage was because they could not control the votes.
Continue reading
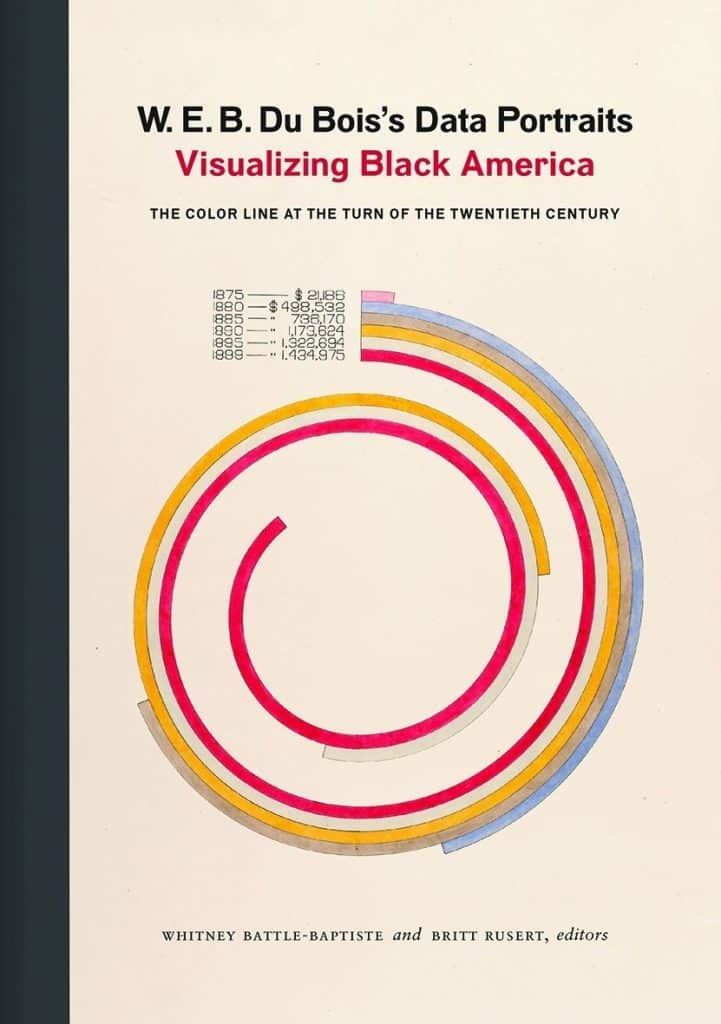
Book — Non-fiction. By the W. E. B. Du Bois Center at University of Massachusetts Amherst. 2018. 144 pages.
W. E. B. Du Bois's Data Portraits is an informative and provocative history, data, and graphic design book first presented at the 1900 Paris Exposition.
Teaching Activity by by the W. E. B. Du Bois Center at University of Massachusetts Amherst and edited by Whitney Battle-Baptiste and Britt Rusert
Continue reading
Teaching Activity. By Adam Sanchez. 2022. Rethinking Schools
A role play about the demise of Reconstruction that helps students get beyond the question “Was Reconstruction a success or failure?”
Teaching Activity by By Adam Sanchez, Illustrator: Nate Kitch
Continue reading
Wyatt Outlaw, a Union veteran who became the first Black town commissioner of Graham, North Carolina, was seized from his home and lynched by members of the Ku Klux Klan known as the White Brotherhood, which controlled the county.
Continue reading
Henry E. Hayne was the first Black student to be accepted to the University of South Carolina’s medical school, a bold act which encouraged other Black students to apply. By 1875, Black men comprised the majority of the student body.
Continue reading
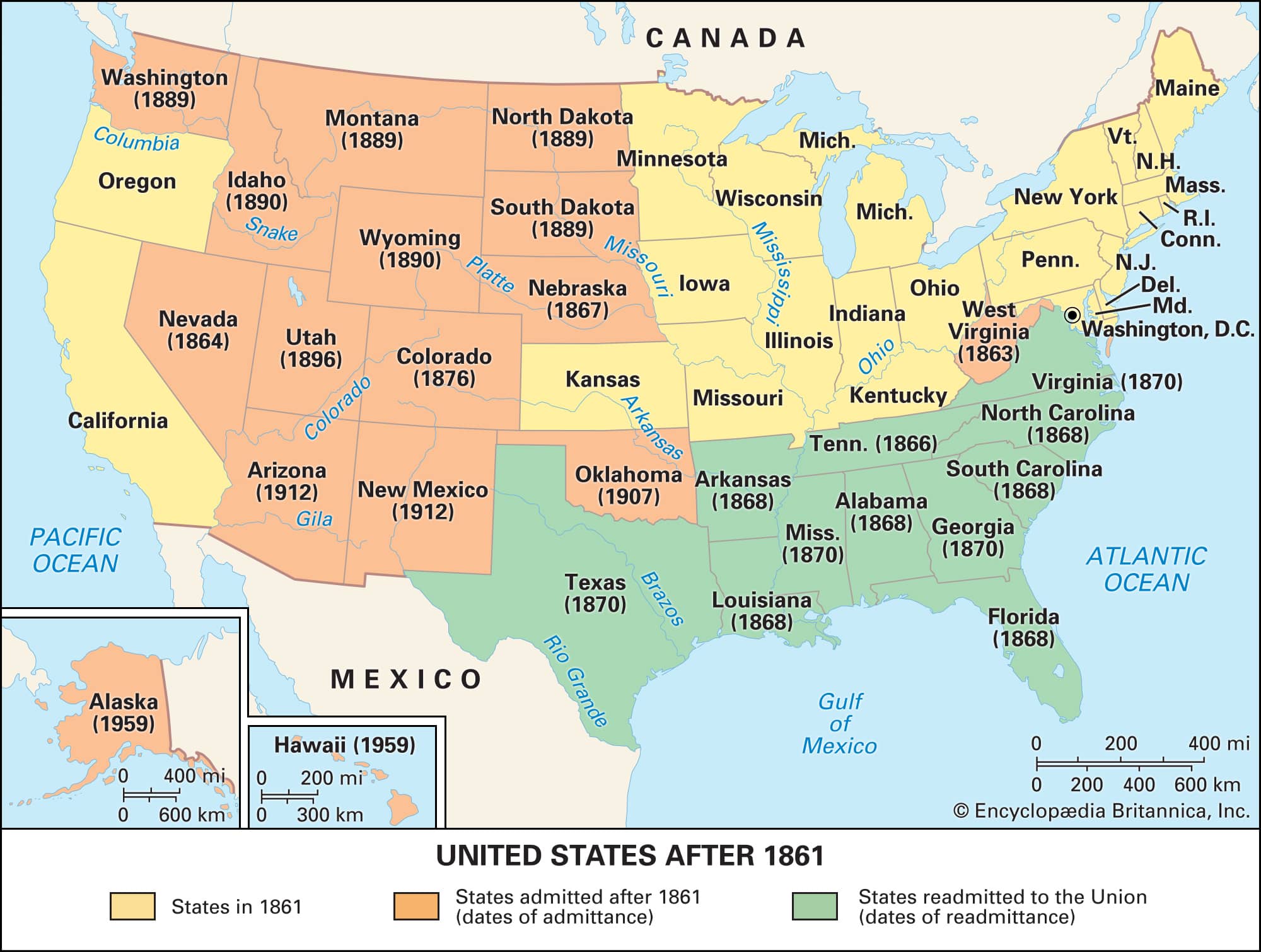
Congress overrode President Andrew Johnson’s veto and passed the first of four statutes known as the Reconstruction Acts, which outlined the process of readmission to the Union.
Continue reading
Digital collection. Documents that help explain how Black people traversed the bloody ground from slavery to freedom between the beginning of the Civil War in 1861 and the beginning of Reconstruction in 1867.
Continue reading
Digital collection. Collections as data and machine learning project examining Jim Crow and racially-based legislation signed into law in North Carolina between Reconstruction and the Civil Rights Movement.
Continue reading
During Reconstruction, Delaware’s Convention of Colored People gathered in Dover to discuss and demand state provisions to educate their children.
Continue reading
Elias Thomson, an African American who lived in Spartanburg, South Carolina, bravely shared testimony detailing violence inflicted against him because he voted for the Republican ticket in the local election.
Continue reading
Juneteenth — June 19th, also known as Emancipation Day — is one of the commemorations of people seizing their freedom from slavery in the United States. Yet, if the right wing has its way, it will be illegal to teach students about Juneteenth.
Continue reading
Edward Alexander Bouchet graduated from Yale University as the sixth person to receive a Ph.D. in physics in the United States.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Kidada E. Williams. 2023. 352 pages.
An account of the brutal white supremacist violence and terror that formerly enslaved people were faced with during Reconstruction.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By E. James West. 2022. 328 pages.
This biography examines the life of historian and activist Lerone Bennett Jr. and his influence on African American culture and history.
Continue reading
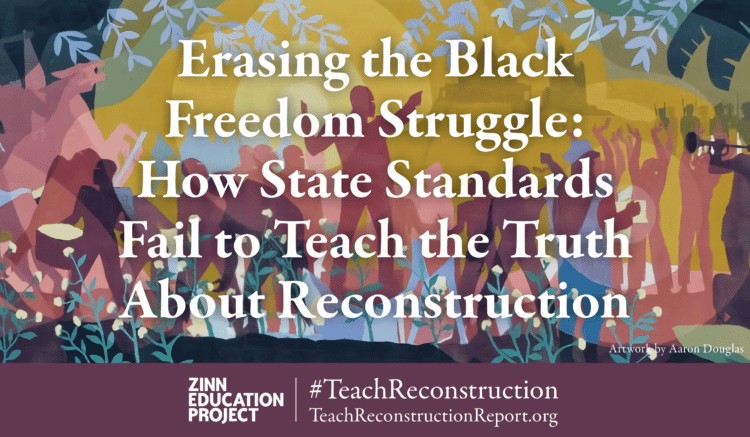
This month we released a printed edition of our national report, Erasing the Black Freedom Struggle: How State Standards Fail to Teach the Truth About Reconstruction. Thanks to the generous support of a donor, we can mail copies of the report to teacher educators, state and school district policymakers, and staff at historical societies.
Continue reading
Teaching Activity. By Mimi Eisen and Ursula Wolfe-Rocca. 47 pages.
A follow-up lesson to “Reconstructing the South,” using primary source documents to reveal key outcomes of the Reconstruction era.
Continue reading
Book — Non-fiction. By Thulani Davis. 2022. 464 pages.
The author traces how people newly freed from bondage created political organizations and connections that mobilized communities across the South during Reconstruction, building on a long tradition of organizing against all odds.
Teaching Activity by Thulani Davis
Continue reading
Teaching Activity. By Adam Sanchez. 2022. Rethinking Schools.
A lesson that help students understand, imagine, and celebrate the Reconstruction period as the first era of Black power in the United States.
Continue reading
Eatonville, Florida is the oldest Black-incorporated municipality in the United States, incorporated toward the end of the Reconstruction era.
Continue reading
Robert Williams and other Black grocers wrote a letter to the Florida Freedmen’s Bureau calling for an end to high taxes levied against them to support former Confederates.
Continue reading
Princeville, North Carolina originated as a resettlement community for freed people and became the oldest incorporated city chartered by African Americans in the United States.
Continue reading
One of the most prominent Black officeholders in Florida during the Reconstruction era, Jonathan Clarkson Gibbs held the positions of Secretary of State and Superintendent of Public Instruction.
Continue reading
Article. By Ana Rosado, Gideon Cohn-Postar, and Mimi Eisen. 2022. 44 pages.
The report includes assessments of education standards in all 50 states and the District of Columbia, along with findings and recommendations for how to improve instruction on Reconstruction.
Continue reading